Mould Manufacturers Near Hebbal
Contact : +91 97404 04503
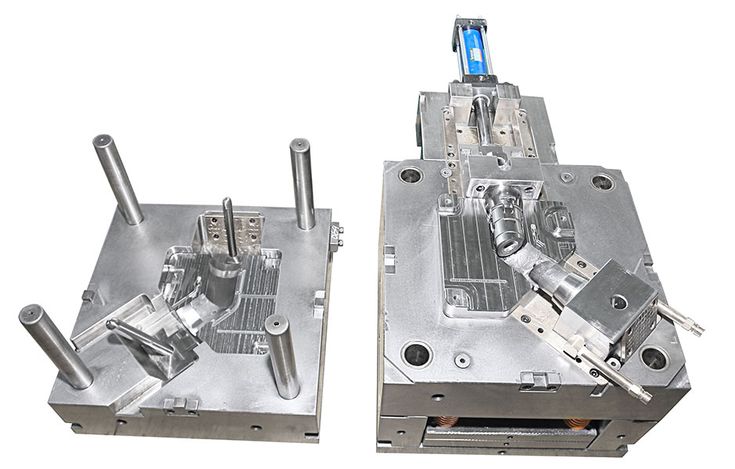
Mould manufacturing is a critical process in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods, enabling the production of complex shapes and designs efficiently. The process involves creating molds, which are tools used to shape materials into a specific form or product. These molds can be made from a variety of materials, such as steel, aluminum, or plastics, depending on the application and requirements.
Types of Moulds
There are several types of molds used in manufacturing, including:
-
Injection Molds: Commonly used for plastic products, injection molds involve injecting molten material into a mold cavity under pressure. The material then cools and solidifies into the desired shape. This is ideal for high-volume production of small to medium-sized parts with intricate details.
-
Compression Molds: Used primarily for rubber or thermoset plastics, compression molds work by placing a pre-measured amount of material into a heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed, and heat and pressure are applied to form the material into the final shape.
-
Die Casting Molds: These molds are used in the production of metal parts, where molten metal is poured into a mold and cooled to form the final product. Die casting is often used for producing high-precision parts, such as engine components or household items.
-
Blow Molds: These are primarily used to create hollow plastic parts, such as bottles or containers. In the blow molding process, air is blown into a heated plastic tube, causing it to expand and fill the mold.
-
Rotational Molds: This type of mold is used for creating hollow, large items like tanks or playground equipment. The mold is rotated on multiple axes while the material inside melts and coats the interior surface to form the shape.
Mould Manufacturing Process
-
Design: The first step in mold manufacturing is the design phase. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software is often used to create precise 3D models of the part or product to be molded. These models are then converted into detailed blueprints that guide the mold-making process.
-
Material Selection: Choosing the right material for the mold is critical to ensure durability, heat resistance, and precision. Steel is often used for high-volume, precision molds, while aluminum is used for lighter, less complex molds. The material chosen also depends on the type of product being produced.
-
CNC Machining: Once the design and material are finalized, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are used to carve and shape the mold components. CNC machines are highly accurate and can handle intricate details, ensuring that the mold meets the design specifications.
-
Mold Assembly: After the individual components of the mold are machined, they are assembled. The mold typically consists of two main parts: the cavity (the negative of the desired part) and the core (which forms the internal features of the part). Additional features such as cooling channels and ejector pins are also integrated at this stage.
-
Testing and Modification: Once the mold is assembled, it undergoes a testing phase where trial runs are conducted to check for flaws in the design or functionality. If necessary, modifications are made to improve the mold’s performance or fix any issues.
-
Production: Once the mold passes testing, it is used for actual production. The material is injected, compressed, or poured into the mold, and the final product is ejected once it has cooled or solidified.
Challenges in Mould Manufacturing
Mould manufacturing is a highly specialized field, and several challenges can arise, including:
- Material wear and tear: Molds can degrade over time, especially in high-volume production, requiring regular maintenance or replacement.
- Design complexities: Some parts may have intricate designs, making it difficult to create molds that meet all the required specifications.
- Cost: The initial cost of mold manufacturing can be high, especially for complex molds. However, the cost per part decreases with high-volume production.
Conclusion
Mould manufacturing is a vital part of modern manufacturing processes. It enables the mass production of high-quality, consistent products in industries ranging from automotive to consumer goods. The process involves a combination of precision design, advanced technology, and material science to create molds that can withstand the rigors of production while delivering the required part specifications.
